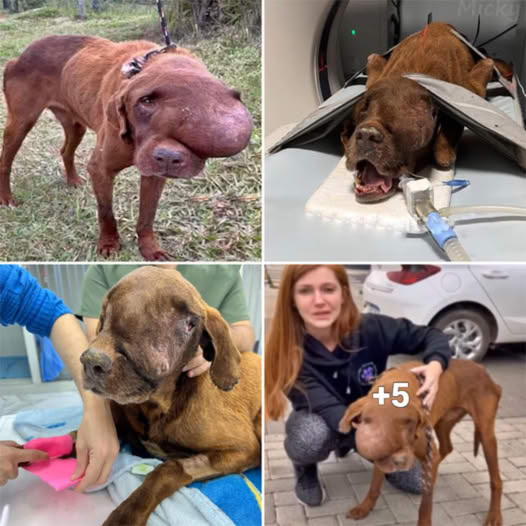
The dog in the images appears to be suffering from a serious condition, possibly an infection, tumor, or other health issue that has resulted in significant swelling, particularly in the facial area. Below is a general overview of potential diseases, symptoms, causes, and treatment options that could relate to such a condition.
Possible Diseases
- Facial Tumors: These can be benign or malignant growths affecting various tissues in the face.
- Abscesses: Infection leading to pus accumulation, often due to bites or wounds.
- Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs that can develop under the skin.
- Dental Disease: Infections in the teeth can lead to swelling in the jaw area.
- Allergic Reactions: Severe allergic reactions can cause swelling, particularly in the face.
Symptoms
- Swelling: Notable swelling in the face, particularly around the mouth or eyes.
- Pain: The dog may show signs of discomfort or pain when touched in the affected area.
- Lethargy: Reduced energy levels and reluctance to play or engage.
- Loss of Appetite: Difficulty eating or a complete refusal to eat.
- Fever: Elevated body temperature, indicating an underlying infection.
- Foul Smell: A noticeable odor from the mouth or swollen area, suggesting an infection.
Causes
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can lead to abscesses or swelling.
- Trauma: Injuries from fights, accidents, or bites that become infected.
- Tumors: Growths that can develop due to genetic factors or environmental influences.
- Dental Issues: Problems with teeth, such as infections or decay, can lead to swelling.
- Allergens: Exposure to allergens that cause an allergic reaction.
Treatment
- Veterinary Examination: A thorough examination by a veterinarian is crucial to diagnose the underlying issue.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays or ultrasounds may be required to understand the nature of the swelling.
- Antibiotics: If an infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed.
- Surgery: In cases of tumors or abscesses, surgical intervention might be necessary to remove the growth.
- Pain Management: Pain relief medications can help improve the dog’s comfort.
- Dental Care: Addressing any dental diseases through cleaning or extractions.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular check-ups to monitor recovery and ensure the issue does not recur.
Conclusion
If you notice symptoms like those described, it is essential to consult a veterinarian promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the prognosis for the dog and enhance its quality of life.